The future of healthcare and technology is defined by precision, connectivity, and personalized care powered by data. Every major advancement, from AI diagnostics to virtual treatment platforms, is transforming how patients access care and how professionals deliver it. These changes mark a shift toward systems that are faster, smarter, and more collaborative. This article explores the innovations reshaping the healthcare landscape and how they prepare future leaders to thrive in a data-driven world.
Key Takeaways
- Technology strengthens healthcare systems by improving diagnostic accuracy, enhancing patient experience, and supporting preventive care.
- Artificial intelligence, telemedicine, and data analytics are driving the next wave of digital health innovation.
- Future healthcare leaders must combine technical literacy with strategic thinking to manage data, improve care, and deliver measurable outcomes.
How Technology Enhances Diagnostic Accuracy and Treatment
Digital innovation continues to reshape the way healthcare professionals detect, diagnose, and treat diseases. Machine learning models and advanced imaging tools now recognize subtle biological patterns that often escape human observation. This level of precision enables earlier intervention, more accurate prognoses, and personalized treatment strategies tailored to each patient’s unique needs.
Technologies such as 3D imaging, smart sensors, and cloud-based medical records are reducing human error and improving efficiency across the entire diagnostic process. When hospitals integrate these digital systems, clinicians can instantly access a patient’s full medical history, test results, and care plans from any department. That kind of connectivity means decisions happen faster, coordination becomes seamless, and patients receive care that is both accurate and timely.
For students preparing to enter the healthcare field, understanding how digital tools amplify, not replace, clinical expertise is essential. Technology serves as a partner in care, turning data into insights that support better judgment, precision, and collaboration. Future leaders who understand these integrations will drive the next era of healthcare innovation.
The Key Ways Technology Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Treatment
Advancements in healthcare technology are redefining precision and reliability in diagnosis and treatment. From AI-assisted imaging to wearable sensors, digital tools now work alongside clinicians to uncover insights that once took days to identify. These innovations strengthen clinical accuracy, improve coordination, and deliver faster, data-driven results for patients.
- Early Disease Detection: AI-driven imaging systems and pattern recognition software help identify diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders at much earlier stages. By comparing new scans to millions of prior cases, these systems detect abnormalities invisible to the human eye.
- Personalized Medicine: Data from wearable devices, genetic testing, and patient histories allows physicians to create individualized treatment plans. This approach improves effectiveness, minimizes side effects, and increases patient satisfaction.
- Automation of Repetitive Tasks: Automated image analysis and digital reporting reduce the time spent on manual documentation. This gives physicians more capacity to focus on patient care rather than administrative tasks.
- Cloud-Based Collaboration: Cloud technology enables specialists across locations to view the same patient data simultaneously. Surgeons, radiologists, and primary care providers can collaborate instantly, improving the accuracy of multidisciplinary decisions.
- Predictive Treatment Planning: Predictive analytics in healthcare uses historical data to forecast how patients might respond to specific therapies. Hospitals use these predictions to design interventions that are more effective and resource-efficient.
- Smart Sensors and Monitoring Devices: Wearable devices and hospital-based sensors collect continuous data on patient vitals. This enables proactive adjustments in treatment, helping prevent complications and emergency readmissions.
- Integration with Robotics: Robotic-assisted surgery brings higher precision, smaller incisions, and faster recovery times. Combined with digital imaging, robots provide surgeons with real-time data that enhances control and safety.
- Enhanced Decision Support Systems: Digital diagnostic platforms provide real-time alerts, evidence-based recommendations, and risk assessments. These systems reduce diagnostic errors and standardize care quality across departments.
Why It Matters for Future Healthcare Professionals
As technology becomes central to modern medicine, future professionals must understand how to apply it responsibly and effectively. Combining data literacy with clinical awareness prepares students to lead in digital-first healthcare environments. Those who can connect human expertise with smart technology will shape the next generation of care delivery.
- Bridging Human and Digital Expertise:
Learning how to interpret data and apply it to real-world clinical settings builds confidence and adaptability. Technology enhances human judgment; it doesn’t replace it. - Building Analytical Confidence:
Familiarity with data interpretation and healthcare analytics helps professionals make informed, ethical, and timely decisions. - Preparing for Industry Change:
As healthcare continues its digital transformation, those who can manage both clinical and technological systems will become indispensable.
Advance your career in the era where healthcare meets technology.
Gain the digital and analytical skills that employers value most. Learn how IBU’s MBA programs connect innovation with leadership in real healthcare environments.
Key Technologies Shaping the Future of Healthcare
As healthcare and technology continue to evolve together, their combined progress is setting a new standard for quality, access, and precision. The future of digital healthcare depends not only on how fast innovations appear but also on how effectively they integrate into clinical settings. From automated systems to real-time monitoring tools, these technologies shape a smarter, safer, and more connected ecosystem for patients and professionals alike. Understanding how each contributes to the broader system helps future leaders navigate digital transformation with confidence and purpose.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Electronic Health Records have become the backbone of modern medical systems. They unify patient information into one accessible source, eliminating redundant tests and inconsistent documentation. EHRs make it possible for physicians, nurses, and specialists to share updates instantly, improving both coordination and accountability.
Beyond operational benefits, EHRs fuel healthcare data analytics. Hospitals can analyze large volumes of patient data to identify emerging health trends, evaluate treatment outcomes, and predict future care demands. For example, aggregated EHR data helps public health officials monitor disease patterns and allocate resources efficiently. When managed properly, EHRs don’t just store data, they drive prevention strategies that reduce long-term costs and improve population health outcomes.
Wearable Health Devices
Wearable technology bridges personal wellness and professional healthcare. Devices such as fitness trackers, ECG patches, and smartwatches collect continuous data about heart rate, oxygen saturation, and physical activity. These measurements enable early detection of irregularities and empower individuals to take active control of their health.
For medical professionals, wearable data creates valuable continuity between appointments. Physicians can review real-time insights, monitor chronic conditions, and adjust care plans proactively. The integration of wearables into healthcare systems also supports digital health innovation by producing reliable data for research and AI-driven analysis. As hardware and sensors advance, wearables are transitioning from lifestyle tools to reliable diagnostic companions that redefine patient engagement.
Robotics and Automation
In hospitals, robotics and automation are no longer experimental; they’re becoming operational standards. Robotic surgical systems allow for ultra-precise incisions, shorter recovery times, and reduced human error. Rehabilitation robots assist patients with mobility exercises, ensuring consistency and accuracy that human repetition alone cannot match.
Automation extends beyond surgery and physical therapy. Administrative automation tools process billing, scheduling, and documentation tasks in seconds, removing manual bottlenecks that often delay care delivery. This efficiency saves time for clinicians and cuts operational costs for institutions. When combined with healthcare automation platforms, robotics help create sustainable, patient-focused systems where technology complements, not replaces, human expertise.
Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Cloud computing supports the digital foundation of modern healthcare. Instead of relying on isolated servers, institutions now use scalable cloud platforms to store, process, and share medical data securely. This connectivity ensures collaboration between hospitals, clinics, and laboratories regardless of location.
Cloud technology plays a central role in research and predictive diagnostics. Researchers can process enormous datasets using artificial intelligence, improving accuracy in genetic analysis, imaging studies, and pharmaceutical testing. It also enhances telemedicine by allowing real-time access to patient files during virtual consultations. With strong encryption and compliance frameworks, cloud platforms ensure both accessibility and security, giving healthcare organizations the agility to adapt as new technologies emerge.
Trends and Benefits of Telemedicine and Remote Healthcare, and Technology
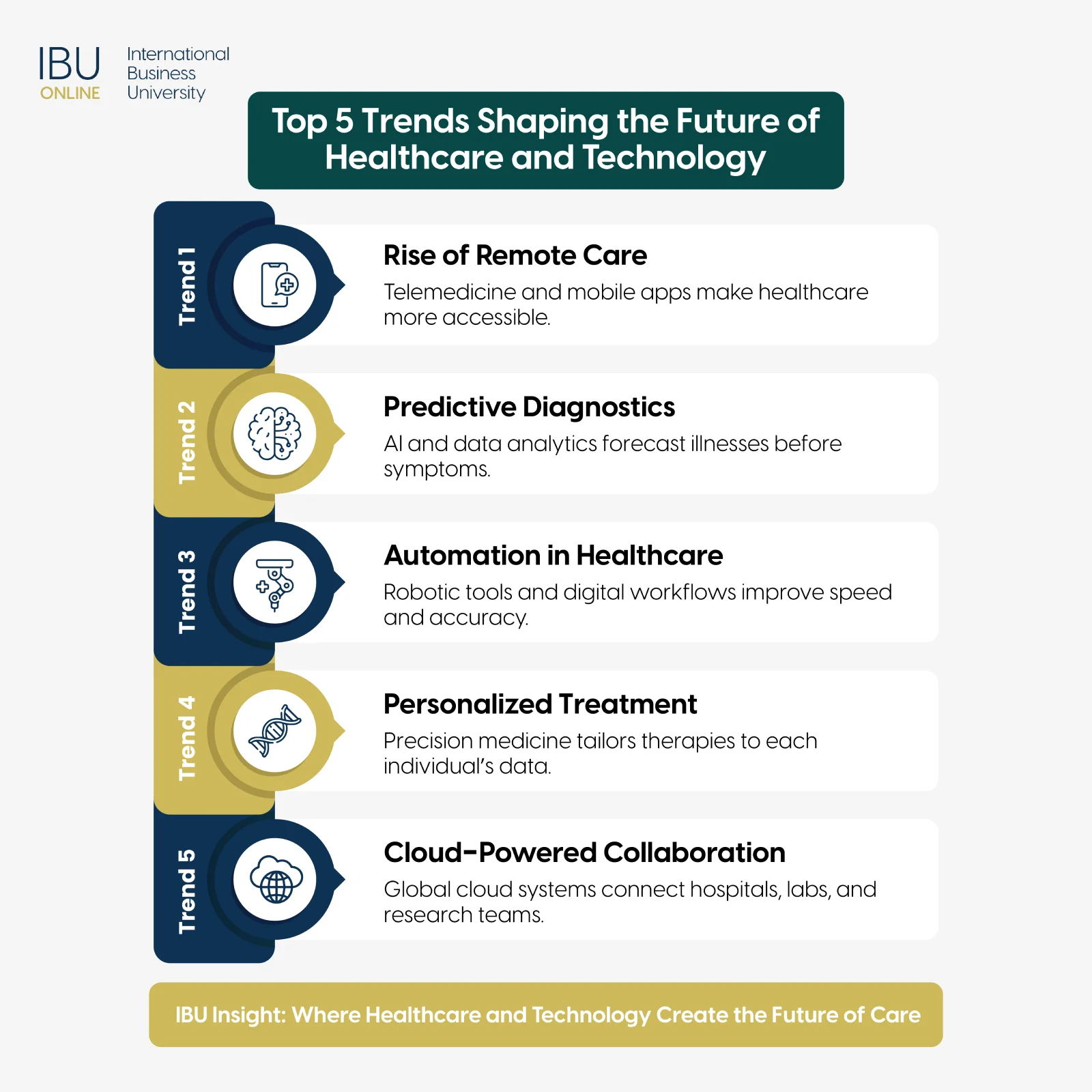
Telemedicine represents one of the most visible results of merging healthcare and technology. It’s reshaping how care is delivered, making consultations, diagnostics, and treatment accessible from almost anywhere. As the global demand for flexible healthcare grows, telemedicine and remote monitoring continue to expand the reach of hospitals and clinics beyond their walls.
For patients, this means convenience and continuity, consistent care without the limits of travel or time zones. For healthcare professionals, it means access to broader populations, better data tracking, and more efficient follow-ups. These trends mark a shift toward personalized, proactive medicine supported by digital tools that prioritize patient outcomes.
Virtual Consultations
Virtual consultations connect patients and physicians through secure video platforms or instant messaging systems. They allow healthcare providers to diagnose minor illnesses, monitor chronic conditions, and provide post-treatment support without requiring physical appointments. This is particularly valuable for patients in rural or underserved communities, where access to specialists can be limited.
From a system perspective, virtual consultations reduce waiting room congestion and improve scheduling efficiency. Healthcare data analytics gathered through these sessions also help track disease outbreaks and patient satisfaction in real time. The success of this model depends on strong digital infrastructure and clear communication standards to maintain quality and confidentiality.
Remote Monitoring Devices
Remote monitoring tools play a critical role in the future of digital healthcare. Devices that track vital signs, glucose levels, or cardiac rhythms send data directly to clinicians for review. Early alerts can trigger timely interventions, reducing hospital readmissions and preventing emergencies.
Hospitals that adopt remote monitoring technology see measurable improvements in resource allocation and patient retention. These devices support healthcare automation by integrating with EHRs and predictive models, allowing medical teams to manage large patient populations efficiently. As connectivity improves through 5G and IoT advancements, remote monitoring will become a central component of preventive and personalized medicine.
Digital Prescriptions
Digital prescriptions, or e-prescribing, replace handwritten notes with secure electronic communication between physicians, pharmacists, and insurers. This reduces transcription errors, prevents medication duplication, and ensures consistent record-keeping.
E-prescribing also speeds up access to medication. Patients can receive their prescriptions instantly after virtual or in-person consultations, and pharmacists can confirm availability without delay. In systems supported by healthcare data analytics, prescription data can even identify population-wide medication trends or potential shortages, helping policymakers plan ahead.
Mobile Health Applications
Mobile health apps empower patients to stay engaged with their care every day. From appointment scheduling to symptom tracking, these apps offer direct access to health education, reminders, and digital consultations.
For clinicians, app-based communication improves patient compliance and data collection. It also supports precision medicine by correlating lifestyle habits with treatment responses. As mobile integration expands, these applications are becoming full-scale digital health ecosystems, connecting users with their healthcare providers, insurers, and even fitness partners through one interface.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Healthcare
AI and machine learning are redefining what’s possible in medicine. They give healthcare professionals tools to predict, diagnose, and treat conditions with unprecedented accuracy. Instead of relying solely on experience, clinicians can now support their judgment with powerful analytical engines capable of processing millions of data points in seconds.
The adoption of these technologies reflects a shift from reactive treatment toward prevention and prediction. Hospitals that integrate AI into their operations see faster diagnostics, fewer errors, and smarter use of resources. For students and professionals entering the field, understanding AI applications is no longer optional; it’s part of modern clinical literacy.
AI in Diagnostics and Imaging
AI has revolutionized medical imaging. Algorithms trained on thousands of radiographs can detect early signs of cancer, fractures, or organ abnormalities often invisible to the human eye. These systems work alongside radiologists, not in their place, serving as a second layer of review that reduces oversight and improves diagnostic confidence.
This accuracy extends to pathology and dermatology as well. AI models can analyze skin lesions, tissue samples, and genetic data to predict disease risks before symptoms appear. Such predictive diagnostics save lives through earlier interventions and more precise treatment planning.
Predictive and Personalized Care
Machine learning’s greatest contribution lies in predictive modelling. By studying patient data, AI identifies risk factors that help clinicians intervene before illnesses escalate. This capability strengthens preventive care strategies and reduces healthcare costs.
At the same time, AI supports personalized treatment. Algorithms assess genetic profiles, lifestyle data, and treatment responses to design therapies tailored to each patient. This approach, central to precision medicine, promises higher success rates and better long-term outcomes. It also deepens the collaboration between data scientists and clinicians, merging analytical skill with clinical experience to create smarter healthcare systems.
Shape the future of healthcare innovation with IBU.
Turn your passion for digital health innovation into a leadership advantage. Join an MBA in Digital Health and Data Analytics program designed for healthcare decision-makers.
Measuring Success: Transforming Data into Measurable Results for Patients
In healthcare and technology, progress must always be measured by outcomes. Digital solutions succeed only when they improve lives, reduce costs, and strengthen the quality of care. That’s why modern institutions use detailed metrics and data-driven evaluation frameworks to assess every innovation’s real-world impact.
Analytics converts vast amounts of healthcare data into usable insights. Hospitals can identify inefficiencies, compare performance across departments, and ensure patient satisfaction stays at the core of every upgrade. This culture of measurement ensures technology serves its ultimate goal, better, safer, and more accessible healthcare.
Patient Outcome Tracking
Digital records make it easier than ever to track patient recovery rates, complication frequencies, and satisfaction scores. These datasets help institutions refine care pathways, set evidence-based benchmarks, and compare their outcomes with regional or international standards.
For example, recovery analytics in post-surgical units can identify which rehabilitation protocols shorten hospital stays without increasing risk. Continuous tracking also builds transparency and accountability, two qualities increasingly demanded by both regulators and patients.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics allows healthcare organizations to look forward rather than backward. By examining years of historical data, predictive tools anticipate patient admissions, resource shortages, and potential health crises.
During flu season or pandemic scenarios, predictive analytics help allocate staff, beds, and medications efficiently. It also supports research into emerging conditions by identifying correlations across populations. This proactive mindset reduces emergency admissions and ensures smoother operations even during peak demand periods.
Resource Optimization
Efficient resource management defines sustainable healthcare. Analytics platforms measure how effectively equipment, staff, and facilities are being used. By reviewing usage patterns, hospitals can decide when to expand departments, adjust staffing, or upgrade technology.
For policymakers, this information provides clarity on national or regional healthcare investment priorities. Balanced resource allocation prevents burnout among professionals, reduces wait times, and delivers consistent patient experiences across all touchpoints.
Continuous Improvement Frameworks
Continuous improvement in digital healthcare depends on feedback loops. Every new system or process should be tested, measured, and refined. Analytics enable hospitals to compare pilot results, validate methods, and scale what delivers results.
These frameworks create a dynamic environment where change is constant and evidence-based. With real-time reporting dashboards, administrators can spot issues early and make corrections quickly. In this way, technology turns healthcare management into a living, learning system, constantly adapting for better care.
Challenges and Opportunities in Healthcare Technology Adoption
Adopting advanced healthcare and technology solutions is not without friction. Integration challenges, financial limits, and human factors often slow progress. Yet every challenge reveals new opportunities for growth, innovation, and collaboration. The future belongs to institutions and leaders who understand both the promise and the process of technological change.
To succeed, organizations must balance vision with execution, introducing tools that align with real clinical needs and building teams ready to adapt. For emerging professionals, this means developing technical fluency alongside leadership and communication skills.
Data Security and Compliance
As digital systems expand, protecting patient data becomes more complex and critical. Healthcare databases are prime targets for cyberattacks, making encryption, multi-factor authentication, and strict access controls mandatory.
Compliance frameworks such as HIPAA and GDPR guide how organizations collect, store, and share medical information. Beyond legal obligations, robust cybersecurity fosters public trust, a key requirement for widespread technology adoption. Ongoing audits and staff awareness programs help maintain these standards and prevent breaches that can jeopardize both privacy and reputation.
Workforce Training
Even the best technologies fail without skilled users. Continuous education ensures healthcare professionals remain comfortable with evolving systems, from AI diagnostics to digital health platforms.
Training programs should combine technical instruction with scenario-based learning that mirrors real workplace challenges. For medical students, early exposure to digital tools during their education builds confidence and fluency. When healthcare workers understand both the “why” and the “how” of technology, they become active participants in progress rather than reluctant adopters.
Integration of Legacy Systems
Many healthcare institutions still rely on legacy systems that weren’t designed for digital interoperability. Integrating these with modern platforms is one of the most persistent challenges in healthcare innovation.
Phased implementation offers a realistic path forward. Institutions can migrate data gradually, pilot new interfaces, and test compatibility before full-scale deployment. This approach minimizes disruptions to patient care and allows IT teams to troubleshoot in real time. Once unified, integrated systems create stronger collaboration, faster communication, and more accurate reporting.
Financial Investment
Introducing digital systems requires initial capital for infrastructure, training, and maintenance. Yet these costs should be viewed as long-term investments rather than expenses. Cloud computing, automation, and AI-powered analytics eventually reduce administrative workload and operational inefficiencies, freeing resources for patient-centred initiatives.
Scalable solutions also enable institutions to expand without rebuilding from scratch. Smaller clinics can start with modular systems that grow with their patient base, ensuring financial sustainability. Governments and private investors increasingly support such transitions through grants and partnerships, recognizing that digital healthcare drives both economic and social progress.
FAQ
Q1: How does technology enhance diagnostic accuracy and treatment outcomes?
Technology supports precise diagnoses through digital imaging, data analysis, and real-time monitoring. It reduces human error and speeds up decision-making, resulting in more effective treatments and better patient recovery.
Q2: What key technologies are shaping the future of digital healthcare?
Artificial intelligence, robotics, wearable devices, and electronic health records are driving healthcare’s digital evolution. Each one contributes to greater efficiency, access, and accuracy in patient care.
Q3: How is telemedicine transforming remote healthcare and technology adoption?
Telemedicine connects patients to providers anywhere, anytime. It increases accessibility, reduces hospital congestion, and supports preventive care by maintaining consistent communication.
Q4: What role do artificial intelligence and machine learning play in healthcare innovation?
They analyze complex medical data to predict diseases, assist in diagnosis, and optimize resource use. Their role is to complement professionals by improving precision and reducing delays.
Q5: How can healthcare leaders measure success through healthcare data analytics?
By defining performance metrics and using analytics to evaluate outcomes. Data-driven decision-making ensures every system upgrade delivers measurable patient and operational benefits.
Q6: What challenges do organizations face in healthcare technology adoption?
Common challenges include data security, system integration, staff training, and funding. Addressing these systematically ensures sustainable digital transformation.
Q7: What opportunities exist for digital health innovation in patient care?
Digital health opens opportunities for early detection, preventive care, and personalized treatment. It empowers patients to manage their health proactively while improving clinical efficiency.
Q8: How can predictive diagnostics improve healthcare outcomes?
Predictive tools analyze past data to anticipate risks before symptoms appear. This allows healthcare providers to intervene early and prevent complications.
Q9: How does precision medicine benefit from healthcare data analytics?
By using individual genetic and lifestyle data, analytics can customize treatments that target specific patient needs. Precision medicine improves effectiveness and reduces side effects.
Q10: How can healthcare leaders prepare for a technology-driven future?
They should invest in digital literacy, encourage collaboration across departments, and prioritize ethical data use. Leaders who understand technology and strategy together will guide healthcare into its next era.
Preparing Healthcare Leaders for a Technology-Driven Future
The intersection of healthcare and technology offers limitless potential for those ready to lead. Tomorrow’s professionals must combine compassion with analytical thinking, mastering both patient connection and digital intelligence. By learning how technology informs decisions, you position yourself to manage systems that improve lives at scale. The next generation of leaders will define the standards for innovation, and your education can prepare you to be among them.
Shape the future of healthcare innovation with IBU..
Turn your passion for digital health innovation into a leadership advantage. Join an MBA in Healthcare Management program designed for tomorrow’s healthcare decision-makers.
